Introducing the GOES-EFD algorithm prototype Version 0.4 focusing on ignition detection timeliness for early warning applications.
Read more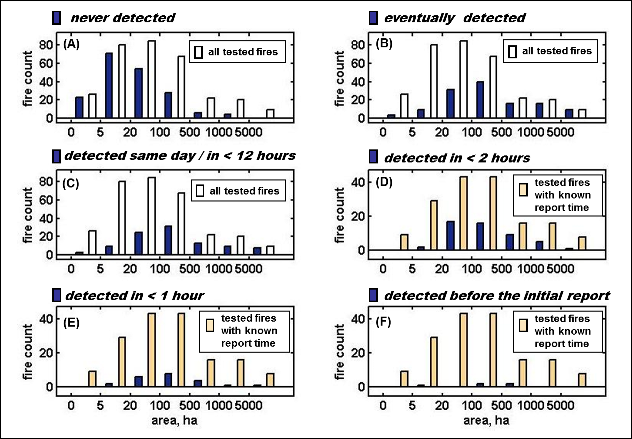
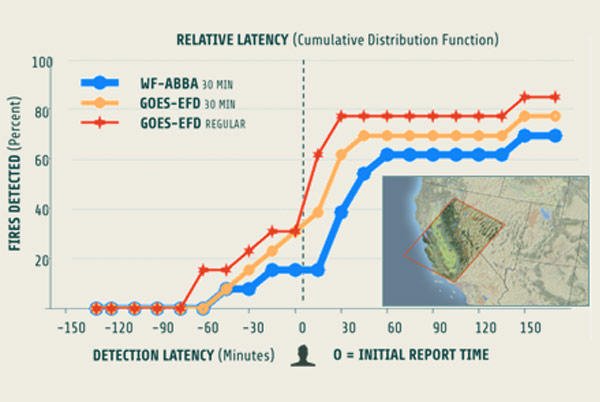
Describing a method for evaluating geostationary wildfire algorithms with respect to timelines and reliability of initial wildfire alerts.
Systematic evaluation of GOES WF-ABBA algorithm over a large number of California wildfires.
WF-ABBA performs best at what it was designed for: consistently re-detecting & monitoring active fires, but not optimal for early warning.
The potential of GOES to shorten wildfire discovery times is currently underutilized.
Read more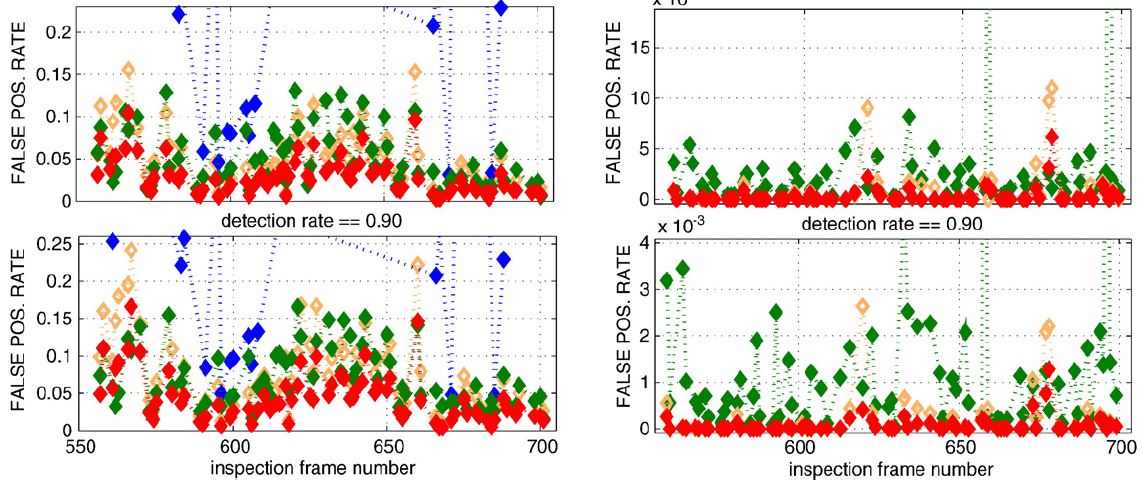
Multitemporal anomaly detection method called Dynamic Detection Model (DDM) shows superior performance when detecting hot spots in MODIS images.
Temporal dimension of the MODIS image sequences is more informative for wildfire detection than spatial context.
Read moreImage construction using multitemporal observations and Dynamic Detection Models
Koltunov, A., E. Ben-Dor, and S.L. Ustin
International Journal of Remote Sensing , 2009
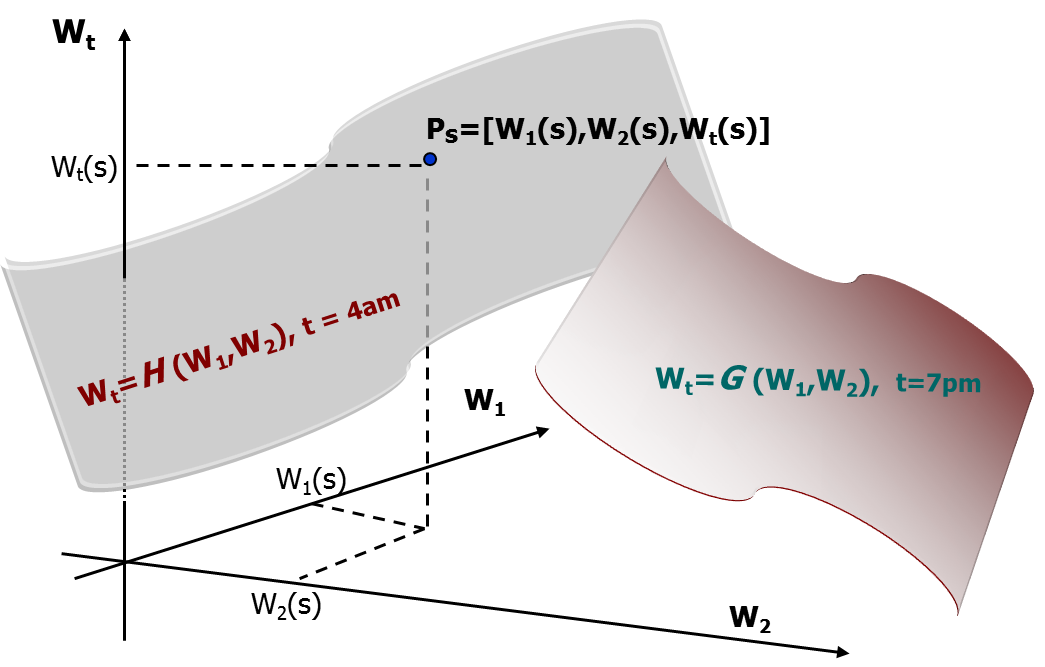
A new method, Dynamic Detection Model (DDM), is presented and mathematically and physically derived and explained.
Temporal invariants and spatial invariants (separable parameters) play a dominant role in forming many remote sensing image datasets, including for instance, images of radiance, brightness temperature, vegetation indices, surface reflectance, and other measurements.
Read more


